Losing power has always been an inconvenience. But these days, with an increasing number of people working from home, maintaining an uninterrupted power supply is vital for both work and play.
The average U.S. household loses power for more than four hours each year. Some areas of the country are prone to even longer blackouts than others—often from weather-related events, such as hurricanes or heavy rainstorms.
On-site battery storage offers a way for you to store solar for use when the grid is down or when your system is not producing. Conventional solar systems rely on inverters to convert direct current from your PV system into alternating current to power your house or send it to the grid. During a blackout, those inverters shut down, which means your PV system can no longer power your house.
Understanding what in-home batteries can do for you
A battery backup system enables you to use stored energy from your rooftop solar panels anytime the power goes out. A backup system also gives you the option of using stored energy during peak-demand periods, when electric rates from your utility are at their highest.
During the day, when your panels are producing, your batteries will recharge. Once they reach full capacity, any additional surplus will flow back to the grid—assuming that your utility offers net metering and enables you to export electricity you don’t use.
Determining your storage needs
When choosing a battery backup system, it’s important to know how much electricity you consume. As the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) notes, the average home consumes 30.5 kWh a day. That includes what you need to run everything from heating and cooling systems to refrigerators and lighting.
A standard emergency backup system would require about 17.1 kWh of energy storage capacity. That would give you sufficient power for lights, refrigerator, and small appliances. In order to handle heavier loads, such as HVAC systems, you would need about 53.6 kWh stored.
Numerous battery options are available for home storage use. Panasonic’s EverVolt batteries, for example, include a module with precisely the capacity needed for a standard back-up installation. The EverVolt system is also modular, which means you can customize a larger capacity backup solution with multiple batteries, depending on your needs.
Choosing AC or DC
The two primary options for battery backup systems are DC coupled and AC coupled. Battery storage capacity is measured in two ways: power capacity and energy capacity. (This short video explains the difference between AC and DC-coupled battery storage systems.)
Generation is often characterized in terms of power capacity, measured as megawatts (MW). But batteries can sustain power output for only so long before they need to be recharged. That duration is the length of time that a storage system can sustain power output at its maximum discharge rate, usually expressed in megawatt-hours (MWh).
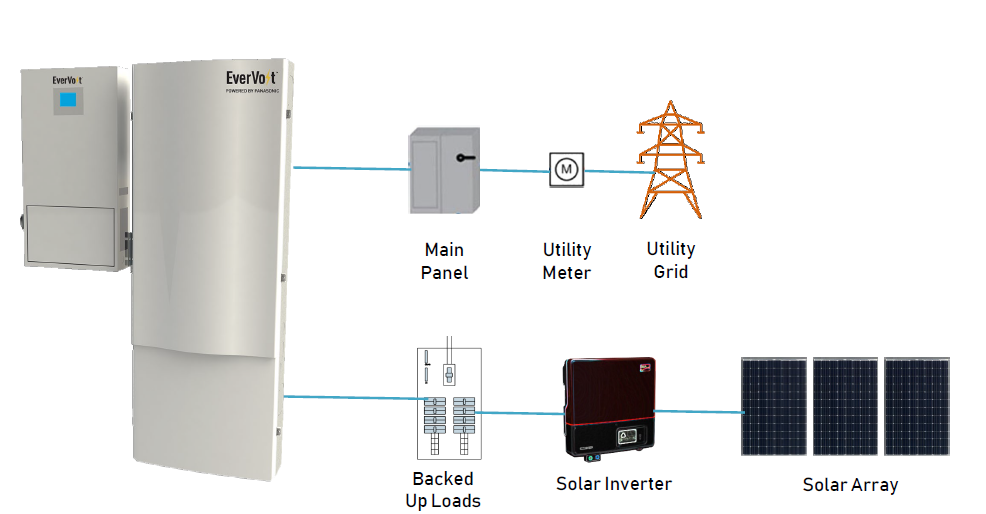
DC-coupled battery systems use one inverter and are often paired with a new solar system for optimizing efficiency. With a DC-coupled system, a battery can be charged directly from your solar panels. An AC inverter is then used to convert the power for household use.
If you’re interested in retrofitting an existing solar installation, an AC coupled system (as shown above) may be your best bet. This type of system can be paired with a wide range of inverters—like those you may already have installed—and can handle AC output from just about any type of PV system. That makes AC batteries a flexible solution for retrofitting an existing solar array.
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis
While battery systems offer a great way to store surplus solar energy on-site, they do require an additional investment. According to Clean Energy Reviews, a general rule of thumb is that a battery system will cost between $800 and $1200 per kWh installed. That means it would cost at least $13,600 to provide enough battery capacity for a standard emergency configuration. Depending on tax breaks and other incentives, your net cost could be lower.
While the economics of installing a battery backup system has to be right for you, one thing is for certain: It's nice to have a bit of sunshine stored for those times that the lights go out.
To learn more about battery storage and how it could be right for your home, visit Panasonic's Green Living blog. For more information about improving your home's resilience with Panasonic EverVolt solar and battery storage bundles, connect with a certified installer.